does a blood test detect testicular torsion|can testicular torsion resolve itself : dealer Testicular torsion is when a testicle rotates, twisting the spermatic cord that provides it with blood and oxygen. Unless the injury is repaired within four to six hours, the loss of blood flow can irreparably damage .
Resultado da Extranet - Adcos
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBFaça o Login na Today 777 hoje e experimente uma variedade de jogos, incluindo slots. Nossa missão é proporcionar uma experiência de jogo justa e divertida para todos os nossos jogadores. Oferecemos Bônus .
Decreased blood flow to the testicle is a sign of testicular torsion. But ultrasound doesn't always detect the reduced blood flow, so the test might not rule out testicular torsion. Surgery.
brix refractometer with atc
Testicular torsion occurs when the testicle rotates on the spermatic cord, which . You might get one or more of these tests to diagnose testicular torsion: Urine test (checks for an infection) An imaging test of your scrotum, usually an ultrasound that uses . Testicular torsion occurs when the testicle rotates on the spermatic cord, which brings blood to the testicle from the abdomen. If the testicle rotates several times, blood flow to .
Testicular torsion is a clinical diagnosis, and patients typically present with severe acute unilateral scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Physical examination may reveal a high-riding. Testicular torsion is when a testicle rotates, twisting the spermatic cord that provides it with blood and oxygen. Unless the injury is repaired within four to six hours, the loss of blood flow can irreparably damage . Testicular torsion refers to the torsion of the spermatic cord structures and subsequent loss of the blood supply to the ipsilateral testicle. This is a urological emergency; .
Testicular torsion is a true urologic emergency, and early identification is critical to prevent the need for testicular amputation. Ultrasound is the ideal imaging modality to .
Testicular torsion is when the spermatic cord above your testicle twists, cutting off blood flow to your testicle. Testicular torsion can happen at any age, but it most often happens to boys ages .
Testicular torsion is an emergency condition due to rotation of the testis and consequent strangulation of its blood supply. Symptoms are acute scrotal pain and swelling, nausea, and vomiting. Diagnosis is based on physical .
Testicular torsion is a time-sensitive diagnosis that requires prompt surgical intervention to avoid testicular ischemia, infertility, and unwanted litigation. When imaging is required, the recommended and most available modality to detect torsion is ultrasonography. In pediatric patients, the use of SMI is supported. Routine testicular self-exams can give you a greater awareness of the condition of your testicles and help you detect changes. Self-exams can also alert you to potential testicular problems. . Depending on the circumstances, your doctor might do a testicular exam followed by a blood test, ultrasound or biopsy. Most changes in your testicles .Testicular torsion is a surgical emergency with a yearly incidence of 3.8 per 100,000 males under the age of 18 [1]. The morbidity associated with testicular torsion is significant as 42% of surgeries result in orchiectomy [1]. However, .
Testicular torsion is when a testicle rotates, twisting the spermatic cord that provides it with blood and oxygen. Unless the injury is repaired within four to six hours, the loss of blood flow can irreparably damage the testicle, causing what is . Testicular torsion, also termed torsion of the spermatic cord, is a relatively common and potentially devastating acute condition resulting from obstruction of the arterial blood supply to the testis. [] Fortunately, this entity is relatively well known, and it usually occurs with enough discomfort to lead to its diagnosis and subsequent testicular salvage.
Blood tests for tumor markers. Some blood tests can help diagnose testicular tumors. Many testicular cancers make high levels of certain proteins called tumor markers, such as alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG). When these tumor markers are in the blood, it suggests that there's a testicular tumor. US can also detect other entities that may mimic symptoms of testicular torsion, including epididymo-orchitis, hydroceles, varicoceles, and testicular masses. . Scrotal scintigraphy is a nuclear study in which a radioisotope is used to demonstrate testicular blood flow. Although it used to be widely utilized starting in 1971, it has been .Main tests for testicular cancer. If the GP refers you to a specialist, you may need more tests and scans to check for testicular cancer. Tests you may have include: blood tests; an ultrasound scan of your testicles; Getting your results. It . Testicular torsion is a twisting of the spermatic cord and its contents and is a surgical emergency affecting 3.8 per 100,000 males younger than 18 years annually. It accounts for 10% to 15% of .
The cremasteric reflex has been reported to be absent in 100% of cases of testicular torsion, making it a potentially useful sign in this diagnosis. However, a significant number of case reports and small case series exist, demonstrating that the test is not 100% specific, and the reflex can be present in cases of testicular torsion.
For example to check for viruses, hormone levels and changes to genes. Your doctor or nurse will talk to you about the different blood tests you will have. You can read more about the blood tests you need in the tests section for your cancer type. Possible risks of having a blood test. Blood sampling (phlebotomy) is a safe test.
testicular torsion signs on examination
Diagnosis of testicular torsion is based on the finding of decreased or absent blood flow on the ipsilateral side. . Physicians should order whichever test is faster and more readily available .Ultrasound imaging is a noninvasive medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. . Ultrasound can often detect an absent or undescended testicle as well. . the twisting of the spermatic cord that contains the vessels that supply blood to the testicle. Testicular torsion is caused by abnormally loose attachments . Figure b. Left scrotal pain in a 22-year-old man 1 week after a skateboard accident. (a) Transverse (TRV) color Doppler US image shows absent flow in the left testis.MID = middle.(b) Transverse gray-scale US image through both testes shows heterogeneous echogenic blood products (arrows) surrounding and compressing the left testis, a finding that accounts for the .
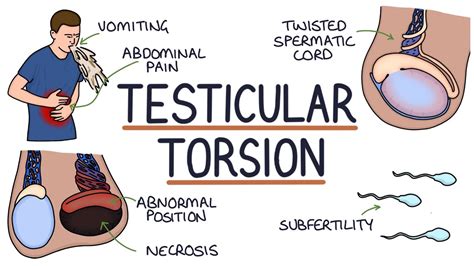
Testicular torsion occurs when a testis torts on the spermatic cord resulting in the cutting off of blood supply. The most common symptom is acute testicular pain and the most common underlying cause, a bell-clapper deformity.The diagnosis is often made clinically but if it is in doubt, an ultrasound is helpful in confirming the diagnosis. The test can show if you have testicular torsion. Testicular torsion is a twisting of the testicle that can cut off blood flow. If ultrasound with color Doppler shows lower blood flow to a testicle than is typical, the testicle is twisted. If blood flow is higher than typical, this can help confirm that you have epididymitis.Diagnosis of testicular and scrotal conditions usually begins with your doctor performing a physical examination and talking with you about your symptoms and health history. Because some symptoms, such as testicular pain and swelling, are common to a number of testicular and scrotal conditions, your doctor will likely order additional tests to help confirm a diagnosis . Lumps inside the testicle are more likely to be testicular cancer. Blood tests. A blood test can detect proteins made by testicular cancer cells. This type of test is called a tumor marker test. Tumor markers for testicular cancer include beta-human chorionic gonadotropin, alpha-fetoprotein and lactate dehydrogenase.
Testicular torsion is a medical emergency that happens when the cord supplying blood to a person’s testicles twists and cuts off the blood supply to the organ. People need surgery to correct this.
9 Testicular Torsion . David Cote. Introduction “Testicular Torsion” by Thomas Newman is licensed under CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 Testicular torsion occurs when the testicl es rotate and the spermatic cord twists. The spermatic cord brings blood flow to the scrotum; therefore, the twisting will reduce the amount of blood getting to the scrotum, which will cause severe pain and . There are several types of testicular trauma, including: Contusion: This is a bruise or a hematoma, a collection of blood beneath tissues. Testicular torsion: This means that the spermatic cord inside the testicle becomes twisted. Because the cord also has blood vessels, it must be untwisted before lack of blood flow leads to tissue death.
↑ Blaivas, M, et al. Emergency evaluation of patients presenting with acute scrotum using bedside ultrasonography. Academic Emergency Medicine. 2001; 8(1):90-93. ↑ Barbosa, JA, et al. Development of initial validation of a scoring system to diagnose testicular torsion in children. The Journal of Urology. 2013; 189:1853-8. ↑ Gordon J, Rifenburg RP. . Spermatic Cord .Keywords: testicular torsion, whirl sign, abdominal pain. INTRODUCTION. The internal and external spermatic arteries travel through the spermatic cord to supply blood to the testicles. Testicular torsion, or the twisting of the testes on the spermatic cord, impedes this supply and is a urologic emergency.
Ultrasound can often detect an absent or undescended testicle as well. It is estimated that approximately three percent of full-term . Ultrasound can identify testicular torsion, the twisting of the spermatic cord that contains the vessels that supply blood to the testicle. Testicular torsion is caused by abnormally loose attachments of . Testicular torsion is a urologic emergency caused by the twisting of the testicle on the spermatic cord leading to constriction of the vascular supply, time-sensitive ischemia, and/or necrosis of testicular tissue. Laher A, Ragavan S, Mehta P, et al. Testicular torsion in the emergency room: A review of detection and management strategies.
A testicular ultrasound is an imaging test that uses high-frequency sound waves to take images . (testicular torsion). Inguinal hernia. How blood flows from your blood vessels into your testicles. . Test Details. How does a testicular ultrasound work? A testicular ultrasound uses a handheld transducer to produce images. A transducer is a . One of the most common tests for testicular pain is an ultrasound. This non-invasive device uses sound waves to create an image of the testicle that can detect injuries, abnormalities, nodules, and tumors. A color Doppler ultrasound can help detect blood circulation problems in cases of testicular torsion.
testicular torsion recovery time
web11 de out. de 2019 · Most of the time, fall-related bumps to the head are minor and don’t require medical attention. . First, some reassuring stats: According to one study on short falls in young children, only .
does a blood test detect testicular torsion|can testicular torsion resolve itself